THE PROS & CONS OF WIRING YOUR BATTERIES IN SERIES VS. PARALLEL
5th Jan 2024
When it comes to wiring your batteries, two common options are available: series and parallel. Each with its own advantages and disadvantages, so it's important to understand them before deciding.

Series
Wiring your batteries in series means that the positive terminal of one battery is connected to the negative terminal of the next, creating a circuit. The voltage of the batteries doubles, while the amperage or capacity remains constant.
For example, if you wire (2) 12V 100Ah batteries in series, the voltage output will be 24V with the amps remaining at 100Ah.
Pros:
- Higher system voltage, leading to lower current draw
- Can use thinner gauge wire due to lower voltage drop
- Increased stability due to less voltage drop
Cons:
- If one battery fails, the entire system shuts down
*before wiring in series, check to make sure your battery accepts series wiring.
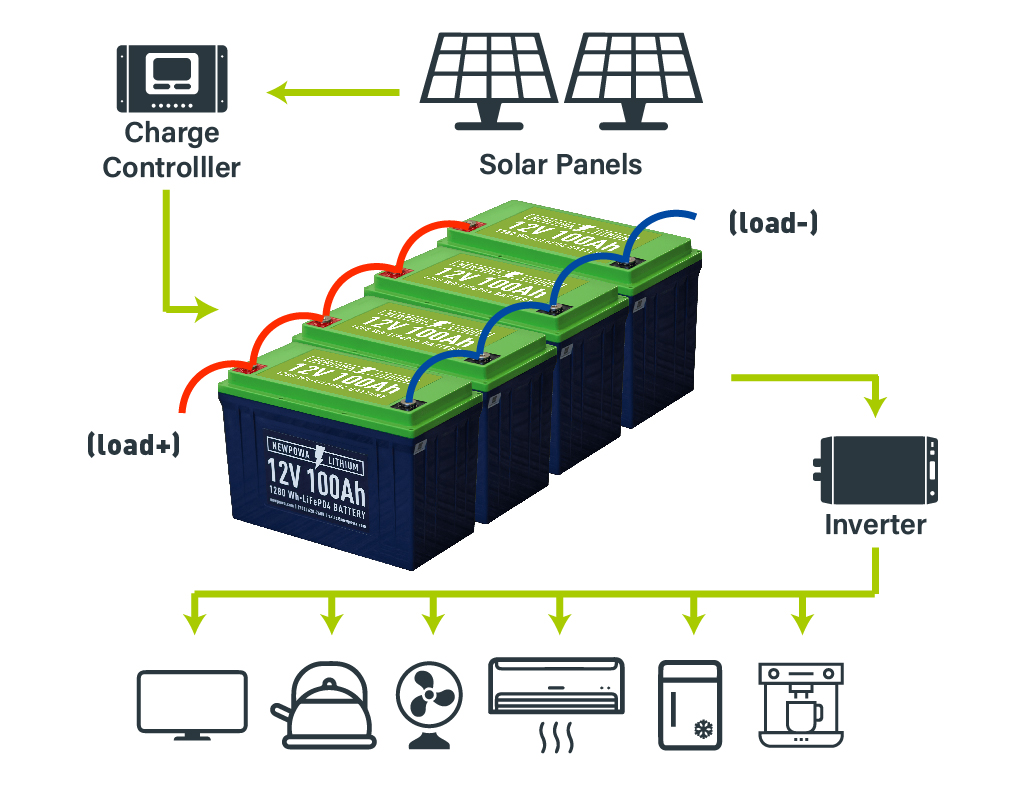
Parallel
Wiring your batteries in parallel means that the positive terminals are connected together, and the negative terminals are connected together, creating a battery bank with an increased capacity.
For example, wiring (2) 12V 100Ah batteries in parallel maintains a voltage output of 12V, but the capacity doubles to 200Ah.
Cons:
- Increased system runtime
- One battery fails, the others will take up the slack & continue to provide power
Longer battery lifespan
Cons:
- Lower system voltage, resulting in higher current draw
- Requirement for thicker gauge wires due to a higher voltage drop
So, what's the best option for your specific needs? It ultimately depends on the application and how much power you require. A series wired battery bank may be the way to go if you need a high-voltage output. If you need a lot of power over a long period of time, wiring in parallel is likely the better option.
Regardless of how you wire your batteries, proper maintenance is crucial to ensure their longevity. This includes regular charging and discharging cycles, avoiding overcharging, and monitoring the voltage and temperature levels. Additionally, the number of batteries wired in series or parallel will depend on the battery and manufacturer. Most lithium batteries are capable of series connections, but not all. So, verify with the battery manufacturer before wiring in series.
In conclusion, both series and parallel wiring options for batteries come with their respective pros and cons. It's important to weigh the pros and cons of your specific application to make the best decision for your needs.
